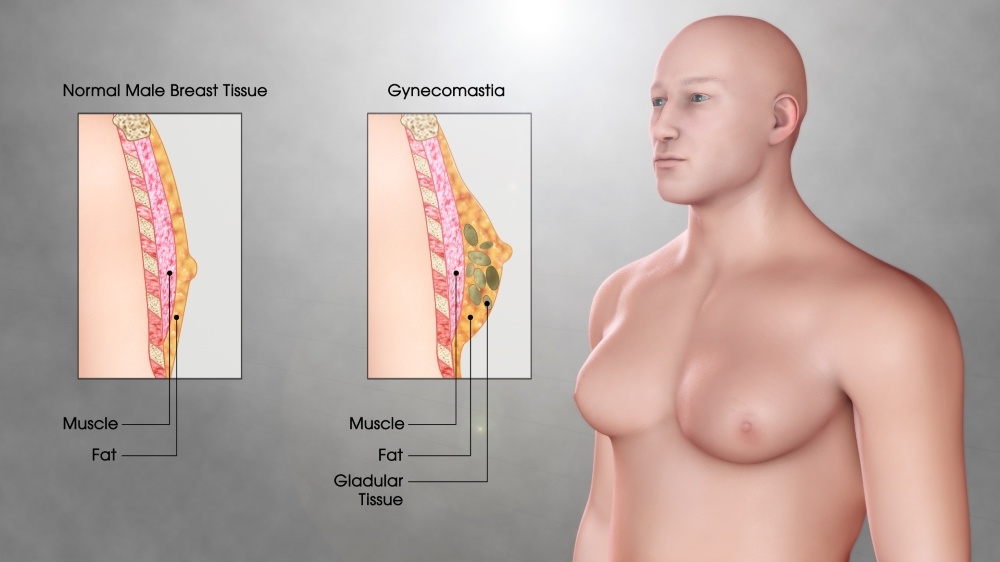
The male breast consists of the nipple and the mammary gland. The mammary gland is small in size and does not grow, remaining atrophic.
Gynecomasty means an increase in the size of the male breast due to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the mammary gland or adipose tissue or both. In some cases, excess skin coexists as well as mastoptosis.
It usually affects both breasts and rarely one. It does not affect health, but appearance makes it difficult for the man in his daily life. Men feel less confident and ashamed and for this reason they may stop sports and bathing during the summer months. Many times the problem can lead to depression, social withdrawal and isolation, as well as to the termination of sexual relations.
Gynecomasty can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal disorders (oestrogen hypersecration, testicle tummors, hepatic and renal failure), drugs that disrupt the ratio of testosterone to estrogen (antihypertensives, antidepressants, amphetamines). In some cases no cause is found and then we talk about idiopathic gynecomasty.
In addition to the unsightly increase in size there may be some tenderness or pain in the chest or (rarely) skin irritation of the area may be caused.
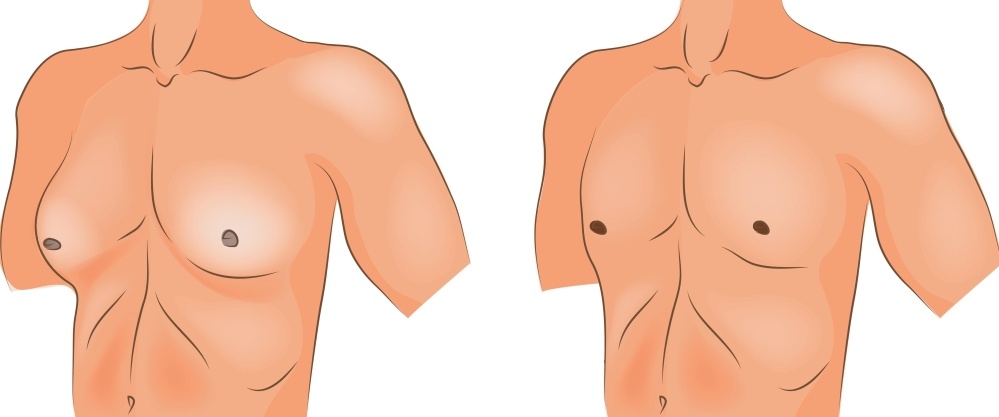
The treatment of gynecomasty is only surgical. Excess fat, the mammary gland and in some cases the excess loose skin are removed during surgery. The surgical incision is made at the borders of the skin with the aureola and is small and indistinguishable.
It can also be treated with liposuction alone or with resection of the mammary gland.
The treatment is usually performed under general anesthesia and the patient is discharged the same or the next day and returns to his activities after two to three days, wearing a special elastic vest.
 English
English  Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά