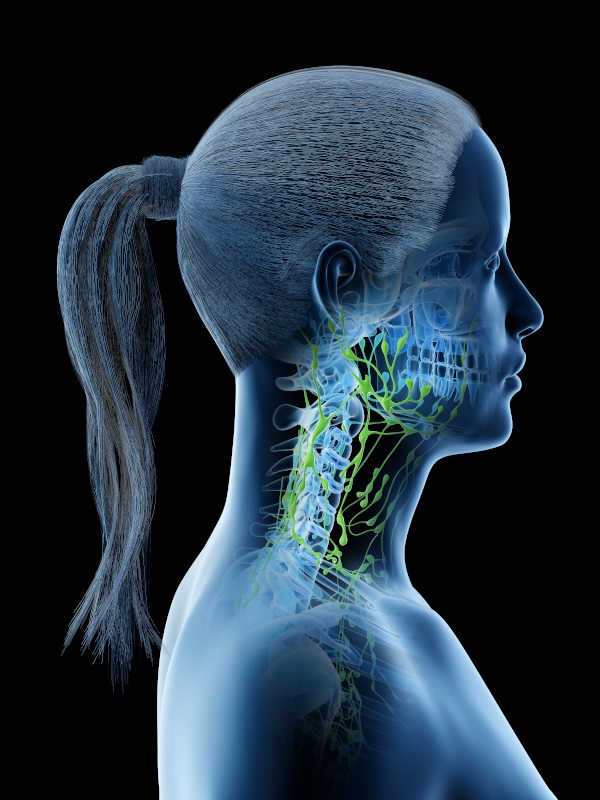
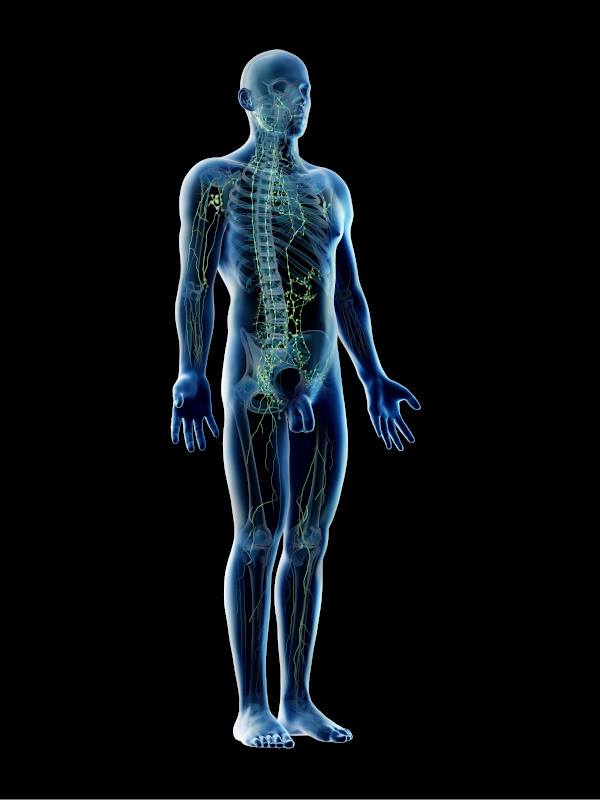
Lymphoma is a form of cancer that affects the immune system. In particular, it is a cancer of the cells of the immune system, called lymphocytes. It occurs when a growing lymphocyte develops a mutation that causes it to either multiply faster than normal or live longer than it should, without responding to regular normal tests.
Risk factors for developing lymphoma include family history, autoimmune diseases, exposure to chemicals and infection with viruses such as Epstein-Barr (infectious mononucleosis), HTL-1 (human lymphotropic virus), HIV (AIDS), hepatitis C and some bacteria.
Lymphoma is divided into two major categories, Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. It can emerge at any age, but is the most common form of cancer in young people.
Symptoms typically include painless swelling of the lymph nodes, often in the neck or armpits, where the lymph nodes conjugate in groups (block). Swollen lymph nodes may also emerge in the groin, abdomen or mediastinum.
Swollen lymph nodes can press on adjacent organs, bones and other structures that cause pain. In addition to swollen lymph nodes other symptoms that are present are swelling in the legs or ankles, night sweats, fever, weight loss, itch, fatigue and loss of appetite.
The diagnosis is made by biopsy and histological examination of a lymph node, bone marrow or other affected organ. The CAT scan helps to stage the disease.
In terms of treatment, there has been a revolution in recent years. The available treatments make the treatment of lymphoma more and more promising. Some types of lymphoma are completely curable, while others are well controlled so that patients' quality of life is not affected.
The main treatments for lymphomas are chemotherapy, immunotherapy (monoclonal antibodies) and radiation therapy, alone or in combination. For slowly evolving non-Hodgkin lymphomas, no treatment may be given initially and the treating doctor may prefer monitoring. In cases of recurrence, a bone marrow transplant is performed.
The role of surgery is in obtaining lymph node biopsies or in surgical excision of blocks of lymph nodes, when important organs are pressed.
 English
English  Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά